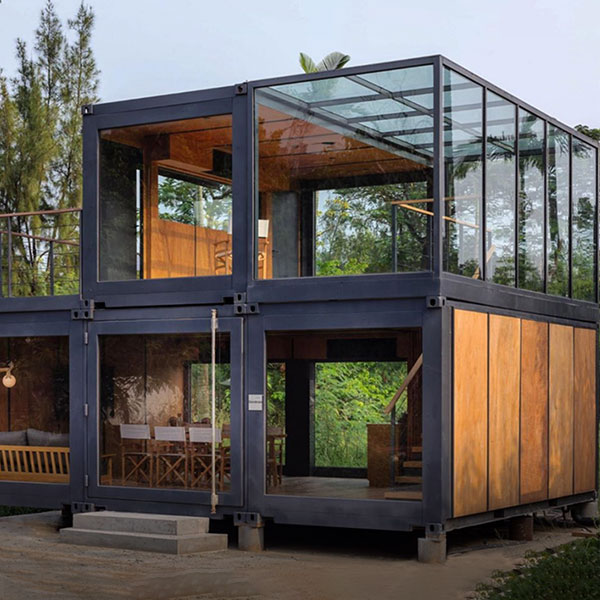
Revolutionizing Industrial Spaces: Prefab House Construction Methods for Facilities
2025-11-21
The industrial landscape is constantly evolving, demanding agility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. When it comes to constructing new facilities or expanding existing ones, traditional methods can often be slow, disruptive, and budget-busting. This is where the power of prefab house construction methods for industrial facilities truly shines. Frankly speaking, the ability to pre-fabricate large components off-site and assemble them rapidly on location offers a compelling alternative that’s reshaping how we build for industry.
Have you ever wondered how some industrial buildings seem to spring up overnight? More often than not, it's a testament to smart design and advanced construction techniques, with prefabrication playing a starring role. In my experience, opting for prefab solutions for industrial facilities isn't just about speed; it’s a strategic decision that impacts everything from project timelines and budget adherence to quality control and site safety.
Understanding the Core Principles of Prefabrication for Industrial Settings
At its heart, prefab construction, also known as offsite construction or modular construction, involves manufacturing building components or entire modules in a controlled factory environment. These finished pieces are then transported to the construction site for assembly. This approach is particularly beneficial for industrial facilities due to the often repetitive nature of their design and the need for robust, functional structures. The key advantages for industrial applications are manifold. Firstly, it significantly reduces on-site labor requirements, which can be a major cost driver and a logistical challenge, especially in remote locations. Secondly, the factory setting allows for stringent quality control, minimizing defects and ensuring consistent standards across all components. This is crucial for industrial environments where structural integrity and operational reliability are paramount. Thirdly, by moving a substantial portion of the construction process indoors, prefab methods are less susceptible to weather delays, leading to more predictable project timelines. It's worth noting that when we talk about "prefab house construction methods for industrial facilities," we're not just talking about small office buildings. We're discussing everything from large manufacturing plants and warehouses to specialized research labs and distribution centers. The scalability and adaptability of prefab systems make them suitable for a vast range of industrial needs.Modular Construction: Building in Three Dimensions
Modular construction is perhaps the most recognized form of prefabrication. In this method, entire sections or rooms of a building are constructed as self-contained units, or modules, in a factory. These modules are then transported to the site and craned into place, where they are connected to form the complete structure. For industrial facilities, modular construction is ideal for creating standardized spaces like offices, control rooms, laboratories, or even entire manufacturing cells. The modules can be designed with integrated MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing) systems, saving further time and complexity on-site. The precision involved in factory fabrication means that modules fit together seamlessly, ensuring a tight, well-sealed building envelope, which is vital for energy efficiency and environmental control in industrial settings.
Panelized Construction: Assembling Flat Components
Panelized construction involves manufacturing wall, floor, and roof panels in a factory. These panels are typically made from materials like steel, concrete, or engineered wood and can be delivered to the site as complete units, often pre-fitted with insulation, windows, and doors. This method is highly efficient for large, open-plan industrial spaces like warehouses or manufacturing floors. The panels are erected sequentially on a prepared foundation, creating the building's shell quickly. Panelized systems offer excellent structural integrity and can be customized to meet specific load-bearing requirements common in industrial environments. The speed of assembly is a significant benefit, allowing for rapid enclosure of the building and protection from the elements, enabling interior fit-out to commence sooner.Exploring Hybrid Approaches and Material Innovations
While modular and panelized systems are distinct, many industrial projects benefit from hybrid approaches, combining elements of both, or integrating prefab components with traditional construction methods. For instance, a steel frame might be erected traditionally, with pre-fabricated wall and roof panels then installed to enclose the structure. This blend can optimize costs and timelines by leveraging the strengths of each method where they are most effective. The choice of materials is also a critical consideration in prefab industrial construction. Steel remains a popular choice due to its strength, durability, and recyclability. Pre-engineered steel buildings (PEBs) are a prime example, offering a highly efficient and cost-effective solution for large industrial spans. Concrete panels, often precast, provide exceptional strength and fire resistance, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications. Increasingly, advanced composite materials and sustainable options are also being explored, offering lighter weight, enhanced insulation, and a reduced environmental footprint.Pre-Engineered Steel Buildings (PEBs): A Dominant Force
Pre-engineered steel buildings are a cornerstone of prefab construction for industrial facilities. These structures are designed and fabricated in sections in a factory, then shipped to the site for assembly. The system typically involves a primary structural frame of steel beams and columns, with secondary framing members supporting the roof and wall panels. The advantages of PEBs are numerous: rapid erection, design flexibility, inherent durability, and relatively low maintenance. They are ideal for a wide range of industrial uses, including factories, warehouses, aircraft hangars, and sports facilities. The ability to span large distances without internal columns is a significant benefit for many industrial processes that require unobstructed floor space.
Advanced Concrete and Composite Solutions
While steel dominates, precast concrete and innovative composite materials are carving out significant niches. Precast concrete offers unparalleled strength, fire resistance, and acoustic insulation, making it ideal for specialized industrial environments where these factors are critical. The precision of precast manufacturing ensures consistent quality and dimensional accuracy. Composite materials, such as those incorporating advanced polymers or reinforced plastics, offer benefits like lighter weight, corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal performance. These are particularly useful in corrosive industrial atmospheres or where weight is a constraint. The development of these materials is continuously expanding the possibilities for prefab industrial construction, offering tailored solutions for demanding applications.The Benefits of Prefab House Construction Methods for Industrial Facilities
Let's delve deeper into why these prefab house construction methods for industrial facilities are gaining so much traction. Beyond the obvious speed and cost savings, there are significant operational and strategic advantages. One of the most compelling benefits is enhanced safety. By performing the majority of the construction work in a controlled factory environment, the risks associated with on-site hazards like working at height, heavy lifting, and exposure to adverse weather are drastically reduced. This leads to fewer accidents and a safer working environment for everyone involved. Predictability and reduced risk are also major draws. In traditional construction, unforeseen site conditions, labor shortages, or material delays can lead to significant cost overruns and schedule slippage. Prefabrication minimizes these variables. The factory environment allows for precise planning, material procurement, and production scheduling, making project outcomes far more predictable. This is invaluable for industrial clients who need to plan production schedules and market entry with certainty. Furthermore, the sustainability aspect of prefab construction is increasingly important. Factory production often leads to less material waste compared to on-site construction. Materials can be precisely cut, and offcuts can be reused or recycled within the factory. Many prefab systems are also designed for energy efficiency, with integrated insulation and air-tight construction contributing to lower operational energy costs for the industrial facility. The flexibility and adaptability of prefab structures are also noteworthy. Many modular and panelized systems are designed for disassembly and relocation, which can be a significant advantage for businesses that anticipate future site changes or expansions. This inherent reusability contributes to a more circular economy approach to industrial building.Addressing Challenges and Future Trends
Despite the overwhelming advantages, it's important to acknowledge that prefab house construction methods for industrial facilities are not without their challenges. Transportation logistics can be complex, especially for very large modules or in areas with limited road infrastructure. Initial design and engineering phases require meticulous planning and collaboration between the client, designer, and manufacturer to ensure all requirements are met before fabrication begins. However, these challenges are being actively addressed. Advances in transportation technology, improved design software, and closer collaboration between stakeholders are smoothing out the process. The industry is also seeing a rise in integrated project delivery (IPD) models, which foster better communication and coordination from the outset. Looking ahead, the future of prefab construction for industrial facilities is incredibly bright. We can expect to see even greater integration of digital technologies, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and virtual reality (VR), to enhance design, planning, and client visualization. Automation and robotics in factories will further improve efficiency and precision. Moreover, the drive towards net-zero buildings and circular economy principles will likely spur further innovation in sustainable materials and modular design for easier deconstruction and reuse. Interest in smart building integration is also growing. Prefabricated systems can be designed to seamlessly incorporate advanced sensor networks, IoT devices, and intelligent control systems from the moment of assembly, creating truly connected and responsive industrial environments. This is a significant step forward for optimizing operational efficiency and predictive maintenance in manufacturing and logistics. In conclusion, prefab house construction methods for industrial facilities offer a powerful, efficient, and increasingly sustainable way to build the infrastructure that drives our economy. Whether through modular, panelized, or hybrid approaches, the ability to construct high-quality, robust, and cost-effective industrial buildings off-site is transforming the sector. It’s an exciting time to witness and be part of this construction revolution.For more detailed information, please visit our official website:prefab industrial buildings
About the author: Alex Chen is a seasoned construction industry analyst with over a decade of experience specializing in innovative building technologies. His expertise lies in evaluating the efficiency and impact of modern construction methods, particularly in the industrial and commercial sectors. Alex is passionate about sustainable building practices and the future of offsite construction.
recommended for you
no data
Get in touch with us
Contact with us
Contact person: Andriy Shulya
Phone: +86 13805366551
E-mail:[email protected]
WhatsApp: +8613805366551
Add: 中国-山东省-潍坊市-新型制造产业园
Copyright © 2012-2026 潍坊青驰房屋有限公司 版权所有 非商用版本
















